Shaping the Future of Commercial Lighting in the United States
Trends that Reflect Broader Industry Movements Towards Sustainability, Energy Efficiency, And Technological Integration
Following the publication of the 2020 U.S. Lighting Market Characterization report and a summary in our previous issue, we looked closely at what characterizes the commercial lighting market. The report offers a detailed analysis of the commercial lighting market, emphasizing significant trends, technology distribution, energy consumption patterns, and the influence of lighting controls. We explored the essential aspects and findings related to commercial lighting in the U.S. as of 2020
Lighting Inventory
Technology Distribution: In 2020, the commercial lighting market was predominantly composed of linear fluorescent and LED technologies, which together constituted 95% of installed lighting. Linear fluorescents are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and established presence, while LEDs are rapidly gaining market share due to superior energy efficiency and longer lifespans.
Building Types: Lighting technology distribution varies across commercial building types, with offices and warehouses significantly influencing overall technology distribution. In 2020, commercial buildings in the U.S. comprised 97.1 billion square feet of floor space. Advanced and energy-efficient lighting solutions are more commonly adopted in sectors with higher operational demands, such as healthcare, education, and offices.
Lamp and Luminaire Types: In commercial settings, linear fluorescent lamps are the most common, especially in office spaces, retail environments, and educational facilities. LEDs are more prevalent in areas requiring high-quality lighting with lower energy consumption, such as healthcare facilities and high-end retail spaces. The variety of lamp and luminaire types is tailored to meet specific needs, balancing light quality, energy efficiency, and operational costs.
Energy Consumption
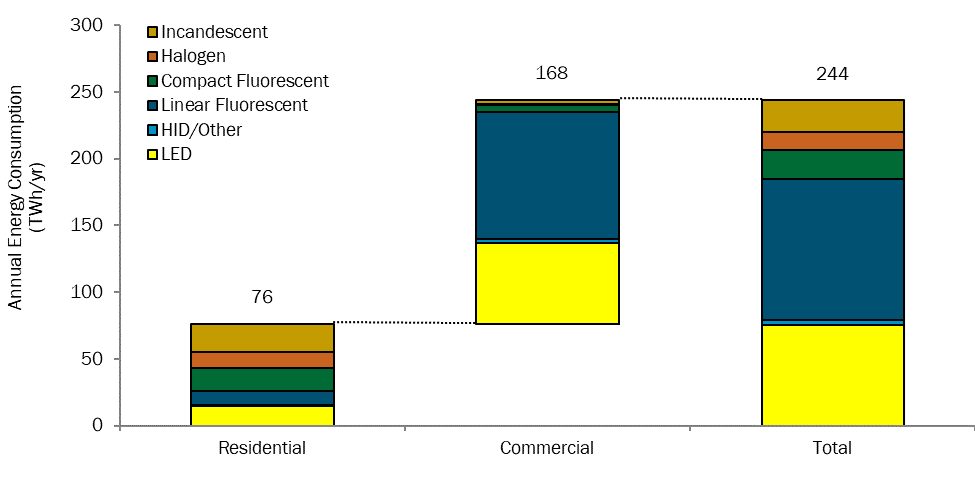
Energy Consumption
Electricity Use: The commercial sector is the largest consumer of lighting electricity in the U.S., accounting for 69% of total lighting electricity consumption despite representing only 20% of the lighting inventory. This disproportionate share is driven by higher lighting intensities and longer operating hours typical of commercial buildings, such as offices, retail spaces, and healthcare facilities.
Technology Contribution: Linear fluorescent and LED technologies are the primary contributors to the commercial sector’s lighting electricity consumption, with linear fluorescents accounting for 43% and LEDs 31%. This highlights the prevalence of these technologies in commercial settings and the importance of ongoing efficiency improvements and technological advancements.
Sectoral Variations: Different commercial subsectors exhibit varying energy consumption patterns. Healthcare facilities, which operate 24/7, have significantly higher lighting energy demands compared to retail stores or office buildings that operate during standard business hours. Each subsector’s specific lighting requirements necessitate tailored approaches to energy management and efficiency improvements.
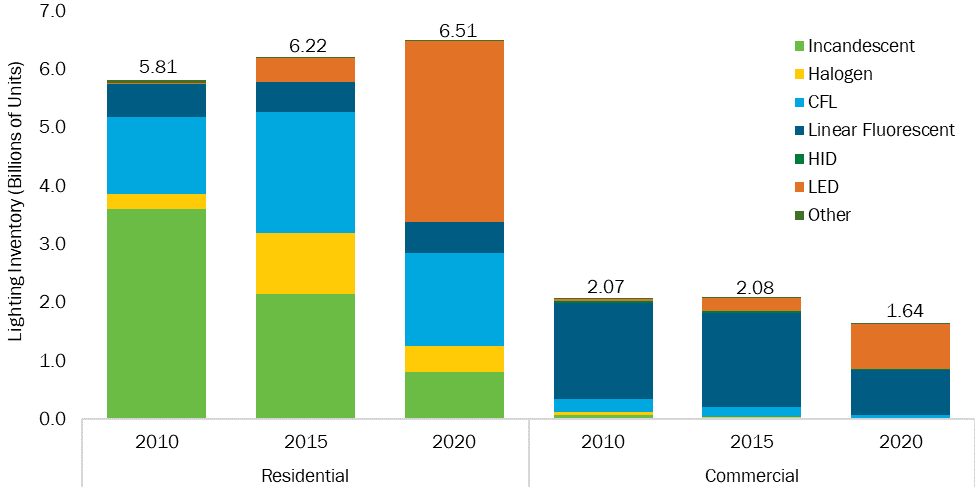
Controls Strategy
Adoption of Controls: There is increasing adoption of lighting control technologies in the commercial sector, such as dimmers, daylighting systems, and energy management systems (EMS). In 2020, over 5,600 commercial buildings utilized EMSs, optimizing lighting usage and reducing energy consumption.
Energy Savings Potential: Implementing control strategies in commercial buildings offers substantial energy savings potential. EMSs enable precise control over lighting systems, ensuring lights are used only when necessary. Other controls, like occupancy sensors and daylight harvesting systems, further reduce unnecessary energy use by adjusting lighting based on real-time occupancy and natural light availability.
Barriers to Adoption: Despite the benefits, barriers to adopting advanced lighting controls persist, including initial installation costs, lack of awareness or expertise in managing sophisticated systems, and the perceived complexity of integrating these technologies into existing infrastructures.
Trends Over Time
Historical Comparison: Comparing lighting market characteristics from 2010, 2015, and 2020 reveals a clear trend towards increased adoption of energy-efficient lighting technologies. There has been a significant decline in incandescent and halogen bulbs, with a rise in LEDs and linear fluorescents, driven by technological advancements, regulatory measures, and growing awareness of the benefits of energy-efficient lighting.
Efficiency Improvements: Continuous improvements in lighting technology efficiency have been observed over the past decade. LEDs have seen dramatic advancements in efficacy, cost reduction, and versatility, making them the preferred choice for new installations and retrofits in commercial buildings. This trend is expected to continue, driven by ongoing innovation and supportive policy frameworks.
Implications for the Future
Market Opportunities: The expanding market for LED lighting and control systems presents significant opportunities for manufacturers, service providers, and building owners. Continued investment in research and development, coupled with supportive regulatory measures and incentives, can accelerate the adoption of energy-efficient lighting technologies, leading to substantial energy savings and cost reductions.
Policy and Incentives: Policymakers play a crucial role in promoting energy-efficient lighting technologies. Incentives such as rebates, tax credits, and funding for retrofit projects can significantly enhance market uptake. Stringent energy efficiency standards and regulations can drive the phase-out of inefficient lighting technologies, further promoting advanced solutions.
Future Research: Ongoing research is essential to explore new lighting technologies and control strategies. Future studies should focus on integrating lighting systems with other building technologies, such as HVAC and smart building management systems, to maximize overall energy efficiency and sustainability.
Commercial Sector Analysis
Lighting Technologies: The commercial sector has seen a substantial shift towards LED lighting, replacing older technologies like fluorescents, incandescents, and high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps. LEDs offer superior energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and reduced maintenance costs, making them the preferred choice for commercial applications.
Distribution of Lamps and Luminaires: In 2020, a large portion of commercial lighting installations comprised LED luminaires. This transition was driven by the need for energy savings, improved lighting quality, and lower operational costs. Detailed data on the number of units installed, their wattage, and operating hours across various commercial subsectors is provided.
Energy Consumption: The widespread adoption of LED lighting in the commercial sector has led to significant reductions in energy consumption. LEDs consume less power and have higher luminous efficacy compared to traditional lighting technologies. The report highlights the energy savings achieved through replacing less efficient lighting with LEDs.
Policy Impact
National and State Policies: National and state policies have significantly promoted the adoption of energy-efficient lighting technologies. Programs offering incentives and rebates for LED installations have accelerated the transition. Regulatory measures have set higher efficiency standards, encouraging the replacement of outdated lighting systems with more efficient alternatives.
Comparison with Previous Years
LED Market Penetration: There has been a significant rise in the market share of LEDs, driven by technological advancements and policy incentives.
Energy Savings: Notable reductions in energy consumption are attributed to the high efficiency of LED lighting.
Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements in LED technology have resulted in better performance, lower costs, and a broader application range.
A Closer Look at the Main Findings
Overview of Commercial Construction Trends: The commercial construction industry has undergone significant changes over the past decade, impacting building design, materials, and energy efficiency. Key drivers include technological advancements, sustainability, and economic factors.
Green Building and Sustainability: Green building practices have gained prominence, with developers and owners prioritizing energy-efficient designs, renewable materials, and reduced environmental impact. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification is widely adopted, emphasizing sustainable construction practices.
Energy Efficiency and Smart Buildings: Energy-efficient technologies are increasingly integrated into commercial buildings. LED lighting, smart HVAC systems, and automated controls help reduce energy consumption. Smart buildings use sensors and data analytics to optimize operations, enhance occupant comfort, and minimize waste.
Adaptive Reuse and Mixed-Use Developments: Adaptive reuse of existing structures is becoming popular, transforming old factories, warehouses, and historic buildings into offices, retail spaces, or residential units. Mixed-use developments combine commercial, residential, and recreational spaces in a single project, creating vibrant urban environments.
Health and Wellness Considerations: Post-pandemic, health and wellness have become critical considerations. Buildings now incorporate features like improved ventilation, touchless systems, and outdoor spaces. Biophilic design principles emphasize connections to nature, promoting well-being.
Technology Integration: Building Information Modeling (BIM) streamlines design, construction, and maintenance processes. Virtual reality and augmented reality aid visualization and collaboration. Drones and robotics assist with site inspections, safety monitoring, and data collection.
Urbanization and Mixed-Use High-Rises: Urbanization drives demand for high-rise mixed-use developments, combining offices, retail, hotels, and residential units in single towers. These vertical cities optimize land use and create vibrant urban cores.
Resilience and Disaster Preparedness: Climate change and natural disasters necessitate resilient construction. Buildings incorporate flood-resistant materials, backup power systems, and disaster recovery plans. Coastal cities prioritize flood barriers and elevated structures.
Supply Chain Challenges and Material Costs: Supply chain disruptions impact material availability and costs, with commodities like lumber and steel experiencing price fluctuations. Contractors seek alternative materials and local suppliers to mitigate risks.
Workplace Evolution and Flexibility: Remote work and hybrid models reshape office design. Flexible layouts, shared workspaces, and advanced IT infrastructure support new work patterns. The demand for adaptable office spaces is rising.
Investment and Financing Trends: Investors focus on sustainable, resilient, and flexible properties. ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria influence investment decisions. Green bonds and financing options support eco-friendly projects.
In Conclusion
The 2020 U.S. Lighting Market Characterization report highlights significant shifts towards energy-efficient technologies, particularly LEDs, and the growing importance of lighting control systems. These trends reflect broader industry movements towards sustainability, energy efficiency, and technological integration, shaping the future of commercial lighting in the United States. The report underscores the importance of continued innovation, supportive policies, and strategic investments to drive further advancements and energy savings in the commercial lighting sector.
DOE Releases 2020 U.S. Lighting Market Characterization Report: Key Insights and Trends
Read the report: 2020 U.S. Lighting Market Characterization | Department of Energy









